Qt Quick 布局 - 响应式布局示例
演示如何使用 LayoutItemProxy 来创建响应式 UI。
本示例展示了如何结合使用 布局 和布局代理项来创建响应式布局。
运行示例
要从 Qt Creator 中运行示例,打开 欢迎 模式并从 示例 中选择示例。有关更多信息,请访问 构建和运行示例。
创建项目
LayoutItemProxy 类型允许在多个布局中使用相同的项,尽管在同一时间只能有一个布局可见。这可以用来创建适应窗口或屏幕大小的响应式布局。
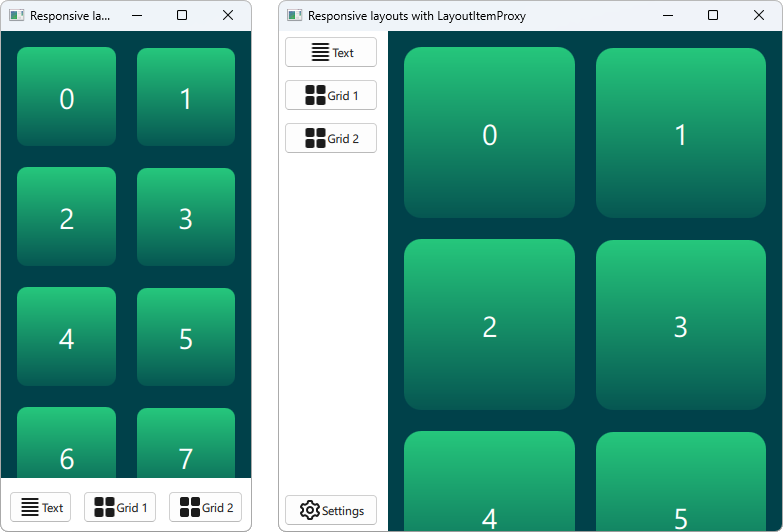
首先,我们需要定义所有应在 UI 中显示的项。我们使用带注释的矩形(AnnotatedRect),这是一个包含一些附加文本的简单矩形。
Rectangle { id: contentItem Layout.fillWidth: true implicitHeight: grid.implicitHeight implicitWidth: grid.implicitWidth color: "#00414A" GridLayout { anchors.fill: parent id: grid columns: 2 anchors.margins: 8 Repeater { model: 18 Rectangle { Layout.fillWidth: true Layout.margins: 8 implicitWidth: 200 implicitHeight: width radius: width / 10 gradient: Gradient { GradientStop { position: -0.2; color: "#2CDE85" } GradientStop { position: 1.2; color: "#00414A" } } Text { color: "#ffffff" font.pointSize: 22 anchors.centerIn: parent text: index } } } } } Button { id: a text: "Text" icon.source: "./icons/text.svg" Layout.fillWidth: true Layout.margins: 3 } Button { id: b text: "Grid 1" icon.source: "./icons/grid.svg" Layout.fillWidth: true Layout.margins: 3 } Button { id: c text: "Grid 2" icon.source: "./icons/grid.svg" Layout.fillWidth: true Layout.margins: 3 } Button { id: d text: "Settings" icon.source: "./icons/settings.svg" Layout.fillWidth: true Layout.margins: 3 }
创建布局
现在,我们可以使用 LayoutItemProxies 声明各种布局,目标为之前声明的项。可以如下定义单个布局:
ColumnLayout { id: smallLayout anchors.fill: parent Flickable { Layout.fillHeight: true Layout.fillWidth: true contentWidth: width contentHeight: gl.implicitHeight clip: true ScrollIndicator.vertical: ScrollIndicator { } LayoutItemProxy { id: gl width: parent.width height: implicitHeight target: contentItem } } RowLayout { Layout.fillHeight: false Layout.fillWidth: true Layout.margins: 5 LayoutItemProxy{ target: a; } LayoutItemProxy{ target: b; } LayoutItemProxy{ target: c; } } }
此代码片段显示了多次使用 LayoutItemProxy 的方式。最简单的方法是将 LayoutItemProxies 添加到布局中,如这里的 RowLayout。此外,我们设置了一个附加属性,它将只影响特定布局中的目标项。此外,我们还可以看到项 d 在第一个布局中没有使用。然后,它自动由第二个布局中的 LayoutItemProxy 隐藏。另外,将其设置为 Flickable 的内容的另一种用法也得到了展示。
另一个布局可以如下声明。
RowLayout { id: largeLayout anchors.fill: parent ColumnLayout { Layout.minimumWidth: 100 Layout.margins: 2 LayoutItemProxy{ target: a } LayoutItemProxy{ target: b } LayoutItemProxy{ target: c } Item { Layout.fillHeight: true } LayoutItemProxy{ target: d } } LayoutItemProxy { Layout.fillHeight: true Layout.fillWidth: false target: contentItem } }
这里展示了 LayoutItemProxies 可以与同一层次结构上的实际 Items 一起使用。通常,LayoutItemProxy 是灵活的,允许嵌套结构的项目和布局。
设置布局
定义完两个布局,即 smallLayout 和 largeLayout 后,我们可以继续设置适应当前应用程序大小的布局。我们为此代码定义了一个新函数,然后在窗口初始化和宽度更改时调用此函数。
function setFittingLayout() { if (width < 450) { smallLayout.visible = true largeLayout.visible = false } else { smallLayout.visible = false largeLayout.visible = true } } onWidthChanged: setFittingLayout() Component.onCompleted: setFittingLayout()
除了在初始化之后调用此函数,我们还可以在声明性代码中隐藏除初始大小正确的布局之外的所有布局。
© 2024 Qt公司有限公司。本文件中包含的文档贡献者是各自版权的所有者。本文件提供的文档是在自由软件基金会发布的GNU自由文档许可证版本1.3的条款下许可的。Qt及其相关标志是芬兰及其它全球国家的Qt公司有限公司的商标。所有其他商标均为各自所有者的财产。
