C
实现矢量图形支持
本节解释了如果目标平台支持,如何实现硬件加速矢量图形支持。
概述
矢量路径
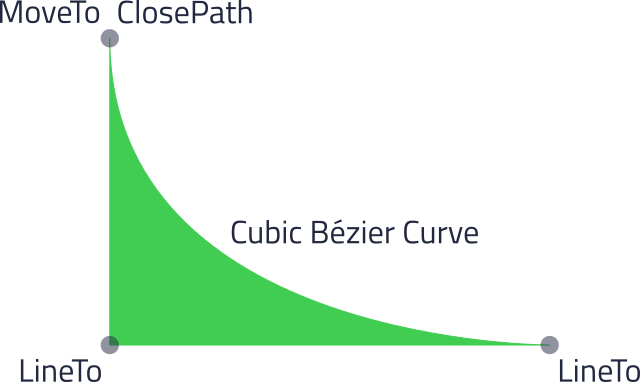
矢量路径通常表示为一系列路径命令。例如,前面图像中的路径可以定义为 SVG 路径
M 21,26.50 V 60 H 69 C 69,60 21,60 21,26.50 Z
其中 M: MoveTo, V: LineTo (垂直), H: LineTo (水平), C: 三次方贝塞尔曲线, Z: ClosePath 是路径命令。数值是每个命令的坐标。因为这些命令是大写字母,它们的参数被视为绝对坐标。
矢量路径表示
平台接口中的矢量路径由Qul::PlatformInterface::PathData类表示。对于前面的示例路径,输出如下
| 函数 | 输出 |
|---|---|
| Qul::PlatformInterface::PathData::segmentCount() | 5 |
| Qul::PlatformInterface::PathData::segments() | Qul::PlatformInterface::PathData::SegmentType [5] { MoveSegment, LineSegment, LineSegment, CubicBezierSegment, CloseSegment } |
| Qul::PlatformInterface::PathData::controlElementCount() | 12 |
| Qul::PlatformInterface::PathData::controlElements() | 示例路径的值存储如下float [12] { x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3, cx1, cy1, cx2, cy2, x4, y4 }坐标值 float [12] { 21.0f, 26.5f, 21.0f, 60.0f, 69.0f, 60.0f, 69.0f, 60.0f, 21.0f, 60.0f, 21.0f, 26.5f } |
注意:垂直和水平线以同时具有 x 和 y 坐标的 LineSegments 存储。
示例图形驱动程序路径
示例图形驱动程序接口使用int32_t表示路径命令和参数来表示矢量路径。它使用 S16.15 固定点格式表示坐标,每个矢量路径都以END命令结束。路径命令是预定义的整数值。早期示例中使用的矢量路径如下
int32_t [] { MOVETO, x1, y1, LINETO, x2, y2, LINETO, x3, y3, CUBIC, cx1, cy1, cx2, cy2, x4, y4, CLOSE, END }坐标转换为 S16.15
int32_t [] { MOVETO, 21.0*(1<<15), 26.5*(1<<15), LINETO, 21.0*(1<<15), 60.0*(1<<15), LINETO, ... }实现矢量图形支持
绘图引擎覆盖
要实现矢量图形支持,派生自Qul::PlatformInterface::DrawingEngine并覆盖以下函数
- Qul::PlatformInterface::DrawingEngine::allocatePath
- Qul::PlatformInterface::DrawingEngine::blendPath
- Qul::PlatformInterface::DrawingEngine::setStrokeProperties
class ExampleDrawingEngine : public PlatformInterface::DrawingEngine { public: ... PlatformInterface::DrawingEngine::Path *allocatePath(const PlatformInterface::PathData *pathData, PlatformInterface::PathFillRule fillRule) QUL_DECL_OVERRIDE; void setStrokeProperties(PlatformInterface::DrawingEngine::Path *path, const PlatformInterface::StrokeProperties &strokeProperties) QUL_DECL_OVERRIDE; void blendPath(PlatformInterface::DrawingDevice *drawingDevice, PlatformInterface::DrawingEngine::Path *path, const PlatformInterface::Transform &transform, const PlatformInterface::Rect &clipRect, const PlatformInterface::Brush *fillBrush, const PlatformInterface::Brush *strokeBrush, int sourceOpacity, PlatformInterface::DrawingEngine::BlendMode blendMode) QUL_DECL_OVERRIDE; };
路径预处理
接下来,创建一个 Qul::PlatformInterface::DrawingEngine::Path 的子类。它可以用于存储特定平台的路径数据。这个 ExamplePath 使用了之前提到的示例图形驱动程序的相同格式。
struct ExamplePath : public PlatformInterface::DrawingEngine::Path { // S16.15 fixed point factor static const int32_t fixedPointFactor = (1 << 15); int16_t fillRule; ExamplePath(const PlatformInterface::PathData *pathData, PlatformInterface::PathFillRule fillRule); void free() { PlatformInterface::qul_delete(this); } const PlatformInterface::PathData *getPathData() { return path; } // Functions to access stored path/stroke elements int32_t *getFillPathData(void) { return fillElements.data(); } int32_t *getStrokePathData(void) { return strokeElements.data(); } // Functions to store fill elements in the platform optimized format inline void addElement(int32_t element) { fillElements.push_back(element); } inline void addElement(float element) { // Convert floating point values to fixed point fillElements.push_back(static_cast<int32_t>(element * fixedPointFactor)); } // Functions to store stroke elements in the platform optimized format inline void addStrokeElement(int32_t element) { strokeElements.push_back(element); } inline void addStrokeElement(float element) { // Convert floating point values to fixed point strokeElements.push_back(static_cast<int32_t>(element * fixedPointFactor)); } // Function to convert fill path data to platform optimized format void processFillPath(); // Functions to return current element counts int32_t fillPathSize() { return fillElements.size() * sizeof(int32_t); } int32_t strokePathSize() { return strokeElements.size() * sizeof(int32_t); } // Functions to remove fill/stroke elements void clearStroke() { strokeElements.clear(); } void clearFill() { fillElements.clear(); } private: // Status flag of the vector path preprocessing bool processingDone; // Path data in the common format const PlatformInterface::PathData *path; // Fill/stroke data format optimized for the platform std::vector<int32_t, Qul::PlatformInterface::Allocator<int32_t> > fillElements; std::vector<int32_t, Qul::PlatformInterface::Allocator<int32_t> > strokeElements; };
可以在结构体构造函数中将 fillRule 转换为特定平台的格式。
ExamplePath::ExamplePath(const PlatformInterface::PathData *pathData, PlatformInterface::PathFillRule fillRule) : fillRule(fillRule == PlatformInterface::PathWindingFill ? HW_PATH_FILL_NON_ZERO : HW_PATH_FILL_FILL_EVEN_ODD) , path(pathData) , processingDone(false) {}
接下来,创建一个函数,它通过 Qul::PlatformInterface::PathDataIterator 遍历路径数据,并将其转换为特定平台的格式。
void ExamplePath::processFillPath() { if (processingDone) return; PlatformInterface::PointF current(0.0, 0.0); PlatformInterface::PathDataIterator it(path); while (it.hasNext()) { PlatformInterface::PathDataSegment segment = it.next(); switch (segment.type()) { case PlatformInterface::PathData::CloseSegment: addElement(static_cast<int32_t>(HW_PATH_CLOSE)); break; case PlatformInterface::PathData::PathSeparatorSegment: break; case PlatformInterface::PathData::MoveSegment: { const PlatformInterface::PathDataMoveSegment *moveSegment = segment.as<PlatformInterface::PathDataMoveSegment>(); addElement(static_cast<int32_t>(HW_PATH_MOVETO)); addElement(moveSegment->target().x()); addElement(moveSegment->target().y()); current = moveSegment->target(); break; } case PlatformInterface::PathData::LineSegment: { const PlatformInterface::PathDataLineSegment *lineSegment = segment.as<PlatformInterface::PathDataLineSegment>(); addElement(static_cast<int32_t>(HW_PATH_LINETO)); addElement(lineSegment->target().x()); addElement(lineSegment->target().y()); current = lineSegment->target(); break; } case PlatformInterface::PathData::QuadraticBezierSegment: { const PlatformInterface::PathDataQuadraticBezierSegment *bezierSegment = segment.as<PlatformInterface::PathDataQuadraticBezierSegment>(); // ... break; } case PlatformInterface::PathData::CubicBezierSegment: { const PlatformInterface::PathDataCubicBezierSegment *bezierSegment = segment.as<PlatformInterface::PathDataCubicBezierSegment>(); // ... break; } case PlatformInterface::PathData::SmallCounterClockWiseArcSegment: { const PlatformInterface::PathDataSmallCounterClockWiseArcSegment *arcSegment = segment.as<PlatformInterface::PathDataSmallCounterClockWiseArcSegment>(); // ... break; } case PlatformInterface::PathData::SmallClockWiseArcSegment: { const PlatformInterface::PathDataSmallClockWiseArcSegment *arcSegment = segment.as<PlatformInterface::PathDataSmallClockWiseArcSegment>(); // ... break; } case PlatformInterface::PathData::LargeCounterClockWiseArcSegment: { const PlatformInterface::PathDataLargeCounterClockWiseArcSegment *arcSegment = segment.as<PlatformInterface::PathDataLargeCounterClockWiseArcSegment>(); // ... break; } case PlatformInterface::PathData::LargeClockWiseArcSegment: { const PlatformInterface::PathDataLargeClockWiseArcSegment *arcSegment = segment.as<PlatformInterface::PathDataLargeClockWiseArcSegment>(); // ... break; } default: QUL_ASSERT(false, QulError_PathData_UnknownSegmentType, segment.type()); return; } } addElement(static_cast<int32_t>(HW_PATH_END)); processingDone = true; }
路径分配
接下来,实现当分配路径句柄时被调用的 Qul::PlatformInterface::DrawingEngine::allocatePath 函数。
PlatformInterface::DrawingEngine::Path *ExampleDrawingEngine::allocatePath(const PlatformInterface::PathData *pathData, PlatformInterface::PathFillRule fillRule) { return PlatformInterface::qul_new<Private::ExamplePath>(pathData, fillRule); }
路径与绘制设备的混合
应接下来实现 Qul::PlatformInterface::DrawingEngine::blendPath 函数。在即将使用 transform 和 blendMode 将路径混合到绘制设备上时调用该函数。结果必须被 clipRect 裁剪,该裁剪矩形位于绘制设备坐标中。此外,sourceOpacity 定义了 0 到 256 的整体透明度范围,其中 256 为完全不透明。
- 如果
fillBrush未设置为nullptr,则路径将根据分配路径时设置的PathFillRule由给定的fillBrush填充。 - 如果
strokeBrush未设置为nullptr,则路径将根据通过setStrokeProperties设置的StrokeProperties进行描边。
void ExampleDrawingEngine::blendPath(PlatformInterface::DrawingDevice *drawingDevice, PlatformInterface::DrawingEngine::Path *path, const PlatformInterface::Transform &transform, const PlatformInterface::Rect &clipRect, const PlatformInterface::Brush *fillBrush, const PlatformInterface::Brush *strokeBrush, int sourceOpacity, PlatformInterface::DrawingEngine::BlendMode blendMode) { Private::ExamplePath *destinationPath = static_cast<Private::ExamplePath *>(path); float matrix[3][3]; toHwMatrix3x3(transform, matrix); // HW_SetClip(clipRect.x(), clipRect.y(), clipRect.width(), clipRect.height()); // HW_BlendMode_t HWblendMode = // (blendMode == PlatformInterface::DrawingEngine::BlendMode_SourceOver ? HW_BLEND_SRC_OVER : HW_BLEND_NONE); if (fillBrush) { destinationPath->processFillPath(); // HW_Path_t hw_path = {..., destinationPath->fillPathSize(), destinationPath->getFillPathData(), ...}; if (fillBrush->pattern() == Qul::PlatformInterface::Brush::LinearGradientPattern) { const Qul::PlatformInterface::GradientStops &gradientStops = fillBrush->linearGradient().stops(); // HW_GradientColorTable_Handle hw_gradientColorTable = nullptr; // hw_gradientColorTable = generateHW_GradientColorTable(gradientStops); // HW_DrawWithLinearGradient(..., &hw_path, destinationPath->fillRule, &matrix, HWblendMode, hw_gradientColorTable, hwLinearGradientParameters(fillBrush->linearGradient()), ...); // As an optimization it might make sense to keep a cache of HW gradient color tables // if (hw_gradientColorTable) // freeHW_GradientColorTable(hw_gradientColorTable); } else if (fillBrush->pattern() == Qul::PlatformInterface::Brush::SolidPattern) { // HW_Draw(..., &hw_path, destinationPath->fillRule, &matrix, HWblendMode, fillBrush->color().value, ...); } } if (strokeBrush) { // HW_Path_t hw_path = {..., destinationPath->strokePathSize(), destinationPath->getStrokePathData(), ...}; if (strokeBrush->pattern() == Qul::PlatformInterface::Brush::LinearGradientPattern) { const Qul::PlatformInterface::GradientStops &gradientStops = fillBrush->linearGradient().stops(); // HW_GradientColorTable_Handle hw_gradientColorTable = nullptr; // hw_gradientColorTable = generateHW_GradientColorTable(gradientStops); // HW_DrawWithLinearGradient(..., &hw_path, destinationPath->fillRule, &matrix, HWblendMode, hw_gradientColorTable, hwLinearGradientParameters(strokeBrush->linearGradient()), ...); // As an optimization it might make sense to keep a cache of HW gradient color tables // if (hw_gradientColorTable) // freeHW_GradientColorTable(hw_gradientColorTable); } else if (strokeBrush->pattern() == Qul::PlatformInterface::Brush::SolidPattern) { // HW_Draw(..., &hw_path, destinationPath->fillRule, &matrix, HWblendMode, strokeBrush->color().value, ...); } } // HW_SetClip(0, 0, screen->width(), screen->height()); }
路径描边
最后,实现 Qul::PlatformInterface::DrawingEngine::setStrokeProperties 函数。可以从 Qul::PlatformInterface::StrokeProperties 访问描边属性,如 LineCapStyle 和 MiterLimit。
void ExampleDrawingEngine::setStrokeProperties(PlatformInterface::DrawingEngine::Path *path, const PlatformInterface::StrokeProperties &strokeProperties) { Private::ExamplePath *destinationPath = static_cast<Private::ExamplePath *>(path); ... }
生成用于描边的路径
可以使用 Qul::PlatformInterface::PathDataStroker 来创建给定路径的描边轮廓路径。这当平台驱动接口不支持描边属性时非常有用。《code translate="no">PathDataStroker 通过继承并重写以下函数来使用:
- Qul::PlatformInterface::PathDataStroker::beginStroke
- Qul::PlatformInterface::PathDataStroker::endStroke
- Qul::PlatformInterface::PathDataStroker::lineTo
- Qul::PlatformInterface::PathDataStroker::moveTo
- Qul::PlatformInterface::PathDataStroker::cubicTo
- Qul::PlatformInterface::PathDataStroker::arcTo
class ExamplePathDataStroker : public PlatformInterface::PathDataStroker { public: ExamplePathDataStroker(ExamplePath *data); protected: void beginStroke() QUL_DECL_OVERRIDE; void endStroke() QUL_DECL_OVERRIDE; void lineTo(float x, float y) QUL_DECL_OVERRIDE; void moveTo(float x, float y) QUL_DECL_OVERRIDE; void cubicTo(float c1x, float c1y, float c2x, float c2y, float ex, float ey) QUL_DECL_OVERRIDE; void arcTo(float x, float y, float rx, float ry, float rotation, bool largeArc, bool clockwise) QUL_DECL_OVERRIDE; private: ExamplePath *destinationPath; PlatformInterface::PointF current; };
实现每个函数的支持以填充路径数据,以针对平台进行优化。这生成了一个表示描边的路径并填充它。
ExamplePathDataStroker::ExamplePathDataStroker(ExamplePath *data) : PathDataStroker(data->getPathData()) , destinationPath(data) {} void ExamplePathDataStroker::beginStroke() { destinationPath->clearStroke(); } void ExamplePathDataStroker::endStroke() { destinationPath->addStrokeElement(static_cast<int32_t>(HW_PATH_END)); } void ExamplePathDataStroker::lineTo(float x, float y) { destinationPath->addStrokeElement(static_cast<int32_t>(HW_PATH_LINETO)); destinationPath->addStrokeElement(x); destinationPath->addStrokeElement(y); current.setX(x); current.setY(y); } void ExamplePathDataStroker::moveTo(float x, float y) { destinationPath->addStrokeElement(static_cast<int32_t>(HW_PATH_MOVETO)); destinationPath->addStrokeElement(x); destinationPath->addStrokeElement(y); current.setX(x); current.setY(y); } void ExamplePathDataStroker::cubicTo(float c1x, float c1y, float c2x, float c2y, float ex, float ey) { // ... current.setX(ex); current.setY(ey); } void ExamplePathDataStroker::arcTo(float x, float y, float rx, float ry, float rotation, bool largeArc, bool clockwise) { // ... current.setX(x); current.setY(y); }
描边路径可以在 Qul::PlatformInterface::DrawingEngine::setStrokeProperties 函数中预先计算。
void ExampleDrawingEngine::setStrokeProperties(PlatformInterface::DrawingEngine::Path *path, const PlatformInterface::StrokeProperties &strokeProperties) { Private::ExamplePath *destinationPath = static_cast<Private::ExamplePath *>(path); Private::ExamplePathDataStroker stroker(destinationPath); stroker.setStrokeProperties(strokeProperties); stroker.stroke(); }
在特定 Qt 许可证下提供。
了解更多信息。
